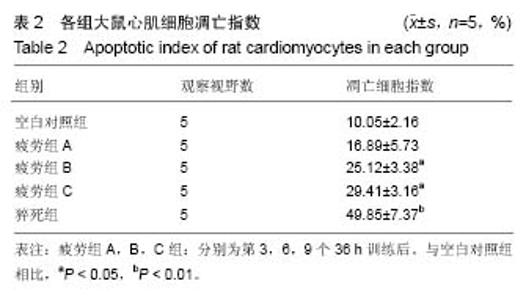
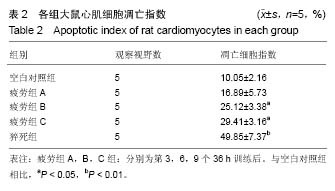
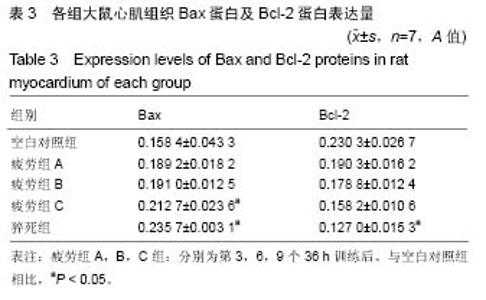
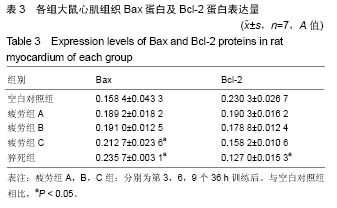
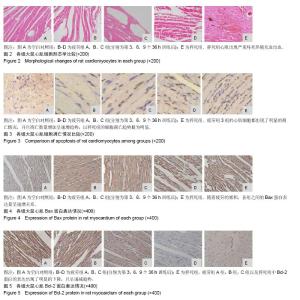
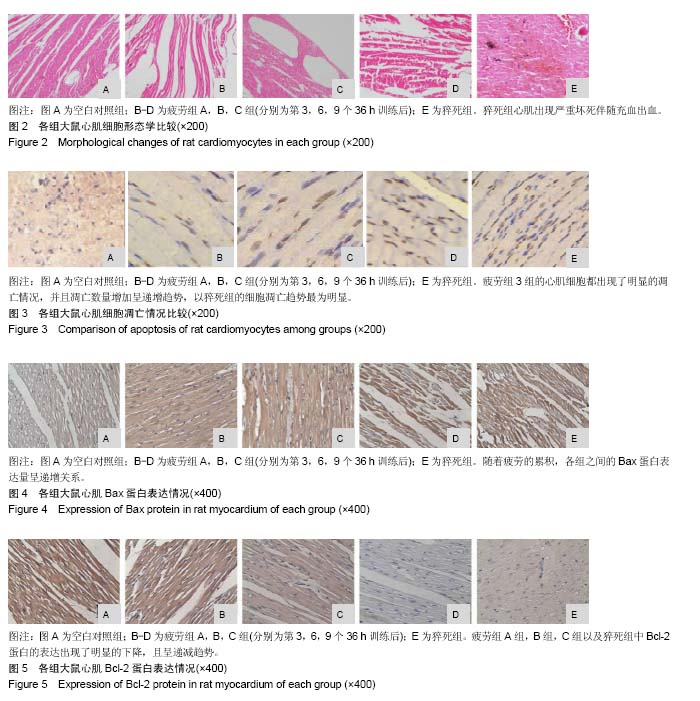
| [1] Mcclean G,Riding NR,Ardern CL,et al.Electrical and structural adaptations of the paediatric athlete's heart: a systematic review with meta- analysis.Br J Sports Med.2018; 52(4):230.[2] 莫轶,韦军.我国运动心脏的诊断现状及进展[J].中国临床新医学, 2018,11(02):208-212.[3] 殷劲,岳建兴,周进等.糖酵解供能运动后“超量恢复区间”的研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2007,33(4):88-91.[4] Carbone A,D'andrea A,Riegler L,etal. Cardiac damage in athlete's heart: When the "supernormal" heart fails.World J Cardiol.2017;9(6):470-480.[5] 钱钰,殷维瑶,李华.过度疲劳状态下运动性猝死模型大鼠甲状腺及心脏功能变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(49): 7356-7363.[6] 钱钰,李华,殷维瑶.过度疲劳状态下运动性猝死大鼠甲状腺功能的变化[J].中国体育科技,2016,6(52):92-98.[7] 阳仁均,殷维瑶,李华.力竭运动性猝死模型大鼠运动皮质Bax、Bcl-2及脑源性神经营养因子的表达变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(49),7377-7383.[8] 万思源,蔡传元,张艳青,等.左甲状腺素和维生素E对甲状腺功能减退症大鼠心肌损伤的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2013,48(1): 21-24.[9] Oláh A, Németh BT, Mátyás C, et alCardiac effects of acute exhaustive exercise in a rat model. Int J Cardiol. 2015;182: 258.[10] 刘峰.姜黄素对力竭运动大鼠心肌抗氧化、糖代谢及细胞凋亡的影响[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2017,38(2):40-46.[11] 翟帅,陈佩林.运动心脏重塑过程中miRNA-350/JNK信号通路的动态变化[J].体育科学,2014,34(5):9-14.[12] 张龙飞,崔玉娟,平政,等.红景天苷对力竭 大鼠心肌线粒体呼吸功能的影响[J].解放军医药杂志,2014,26(11):1-5.[13] 徐鹏,康亭,曹雪滨,等.力竭运动后不同时相大鼠心电图、心功能变化及Nrf2的作用[J].中国应用生理学杂志, 2016,32(2): 146-151.[14] 公雪,李晓燕.力竭运动对心肌组织结构及功能影响的研究进展[J].心血管病学进展,2016,37(4):435-440.[15] 赵小辉.红景天苷对急性力竭运动大鼠的心脏保护作用及机制研究[J].中国妇幼健康研究,2016,27(2):261.[16] 王永良,刘忠民,刘眉眉,等.不同负荷游泳运动对老龄大鼠心肌细胞形态及Bax、Bcl-2蛋白表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2017, 4(37):1857-1859.[17] Chatard JC,Mujika I,Goiriena JJ,etal.Screening young athletes for prevention of sudden cardiac death: Practical recommendations for sports physicians.Scand J MedSci Sports.2016;26(4):362-374.[18] 费萍燕,彭生,费民忠,等.miR7在心肌细胞缺氧复氧模型中的表达及对心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].使用预防医学,2018,25(2): 195-198.[19] 孙晓娟,力竭运动损伤模型大鼠运动预适应后心脏STAT3和Caspase-3的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(40): 6450-6454.[20] 田阁,徐昕,李国平.C/EBPβ在预防心源性运动猝死中的潜在作用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(3):263-266. |